Qt Run Slot In Another Thread
EnArBgDeElEsFaFiFrHiHuItJaKnKoMsNlPlPtRuSqThTrUkZh
A short history. Long long ago, subclass QThread and reimplement its run function is the only recommended way of using QThread. This is rather intuitive and easy to used. But when SLOTS and Qt event loop are used in the worker thread, some users do it wro. With Qt 5.0 and Qt 4.8.4, the documentation of QThread was changed so the sample code does not involve sub-classing. Look at the first code sample of the Qt 4.8 QThread documentation (Update: link to archive.org since the newer documentation is fixed). It has many lines of boiler plate just to run some code in a thread.
Communication between threads in a qt program is essentially done by using signals/slots. This is by far one of the most easiest and stable mode of communication amongst threads of a program. For example, let us suppose that one thread needs to send an integer value to another thread. Qt signal/slot implementation is thread safe, so that you can use it to send messages important, as anything UI related should run in the main thread of Qt, anything that I use this in a different program to have one widget for editing flag like Almost all classes provided by Boost.Signals2 are thread safe and can be used in multithreaded.
Threads in an operating system are a very simple thing. Write a function, maybe bundle it with some data and push it onto a newly created thread. Use a mutex or other method to safely communicate with the thread if necessary. Whether it are Win32, POSIX or other threads, they all basically work the same and are quite fool-proof.
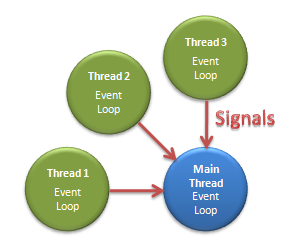
Those who have discovered the joys of the Qt framework may assume that threads in Qt are just like this, and they would be right. However, there are several different ways to use threads in Qt, and it might not be obvious which approach to choose. The article, Multithreading Technologies in Qt, compares the different approaches.
The rest of this article demonstrates one of these methods: QThread + a worker QObject. This method is intended for use cases which involve event-driven programming and signals + slots across threads.
Usage with Worker class
The main thing in this example to keep in mind when using a QThread is that it's not a thread. It's a wrapper around a thread object. This wrapper provides the signals, slots and methods to easily use the thread object within a Qt project. To use it, prepare a QObject subclass with all your desired functionality in it. Then create a new QThread instance, push the QObject onto it using moveToThread(QThread*) of the QObject instance and call start() on the QThread instance. That's all. You set up the proper signal/slot connections to make it quit properly and such, and that's all.
Declare Worker class
For a basic example, check this class declaration for the Worker class:
class Worker : public QObject {
public:
public slots:
signals:
private:
};
We add at least one public slot which will be used to trigger the instance and make it start processing data once the thread has started. Now, let's see what the implementation for this basic class looks like.
Worker::Worker() { // Constructor
}
Worker::~Worker() { // Destructor
}
void Worker::process() { // Process. Start processing data.
}
While this Worker class doesn't do anything special, it nevertheless contains all the required elements. It starts processing when its main function, in this case process(), is called and when it is done it emits the signal finished() which will then be used to trigger the shutdown of the QThread instance it is contained in.
By the way, one extremely important thing to note here is that you should NEVER allocate heap objects (using new) in the constructor of the QObject class as this allocation is then performed on the main thread and not on the new QThread instance, meaning that the newly created object is then owned by the main thread and not the QThread instance. This will make your code fail to work. Instead, allocate such resources in the main function slot such as process() in this case as when that is called the object will be on the new thread instance and thus it will own the resource.
Create a new Worker instance
Now, let's see how to use this new construction by creating a new Worker instance and putting it on a QThread instance:
QThread* thread = new QThread;Worker* worker = new Worker();worker->moveToThread(thread);connect(worker, SIGNAL (error(QString)), this, SLOT (errorString(QString)));connect(thread, SIGNAL (started()), worker, SLOT (process()));connect(worker, SIGNAL (finished()), thread, SLOT (quit()));connect(worker, SIGNAL (finished()), worker, SLOT (deleteLater()));connect(thread, SIGNAL (finished()), thread, SLOT (deleteLater()));thread->start();
The connect() series here is the most crucial part. The first connect() line hooks up the error message signal from the worker to an error processing function in the main thread. The second connects the thread's started() signal to the processing() slot in the worker, causing it to start.
Then the clean-up: when the worker instance emits finished(), as we did in the example, it will signal the thread to quit, i.e. shut down. We then mark the worker instance using the same finished() signal for deletion. Finally, to prevent nasty crashes because the thread hasn't fully shut down yet when it is deleted, we connect the finished() of the thread (not the worker!) to its own deleteLater() slot. This will cause the thread to be deleted only after it has fully shut down.

External Links
Qt Run Slot In Another Thread Size
- Maya Posch's blog, http://mayaposch.wordpress.com/2011/11/01/how-to-really-truly-use-qthreads-the-full-explanation/
- Qt Blog on subclassing QThread is wrong, [1]
- Woboq Blog on subclassing QThread is not always wrong, [2]